Talavera Poblana is an exquisite type of pottery whose history goes back hundreds of years. The lovely and beautiful colonial city of Puebla, located just 70 miles from Mexico City, is home to this world-renowned art form. In addition to purchasing authentic Talavera pottery in Puebla, there are many reasons to visit the city, including sampling its fabulous regional cuisine. Some of Puebla’s delectable dishes include their famous mole poblana sauce as well as the seasonal delicious dish of chiles en nogada. Additionally, the historic center of Puebla has been named a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Undoubtedly, one of the reasons for this honor is due to the absolutely stunning tile work that decorates the town’s historic colonial buildings.
Talavera Poblana is an exquisite type of pottery whose history goes back hundreds of years. The lovely and beautiful colonial city of Puebla, located just 70 miles from Mexico City, is home to this world-renowned art form. In addition to purchasing authentic Talavera pottery in Puebla, there are many reasons to visit the city, including sampling its fabulous regional cuisine. Some of Puebla’s delectable dishes include their famous mole poblana sauce as well as the seasonal delicious dish of chiles en nogada. Additionally, the historic center of Puebla has been named a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Undoubtedly, one of the reasons for this honor is due to the absolutely stunning tile work that decorates the town’s historic colonial buildings.
Mexico has a rich and long history with producing ceramics, predating the arrival of the Spanish by several centuries. Stunning pre-Columbian artifacts from its many civilizations attest to this fact. The indigenous peoples of Mexico, long acquainted with making items from clay, had their own distinct method of producing earthenware, one which did not involve glazing or the use of the potter’s wheel.
Shortly after Puebla was founded in 1531, the Spanish feverishly began building churches, monasteries and convents. To decorate these buildings, craftsman from the city of Talavera de la Reina, located in Spain, were commissioned to come to the New World to produce fine tiles as well as other ceramic ware. In addition, these same craftsman were to teach the indigenous artisans their technique of Majolica pottery, in order to increase production levels.
The tradition that the Spanish craftsmen brought from Talavera de la Reina to the New World has a fascinating history. During the 8th century, the Moors from Northern Africa conquered Spain and with their arrival, the customary blending of cultures occurred. One such consequence was the introduction of Majolica pottery, an art form known for its beautiful glazes and intricate design work. A major component of Majolica is its glazing technique which contains tin as an ingredient. This particular type of glaze provides a creamy white background that is ideal for applying design.
Spanish craftsman from Talavera de la Reina embraced the techniques of Majolica and also added to the art form. Chinese and Italian influences were incorporated and guilds of craftsmanship, where strict adherence to technique were required, were formed. This dedication was brought from Spain to Mexico. Guilds were summarily established in Mexico with appropriate standards and regulations. The indigenous craftsmen incorporated their artistic heritage with the techniques of Majolica pottery. A beautiful marriage was formed between the old world and the new, and Puebla became the birthplace of an exquisite art form known as Talavera Poblana.
An elaborate process is involved in making a piece of Talavera pottery. First, comes the selection of the clay, which is chosen from the area of Puebla and nearby vicinities. The clay found in this region is known for its fine quality. After a detailed process of washing and soaking the clay, it is then hand-formed or shaped on a potter’s wheel into its desired form. Next, it is allowed to dry in the sun for a matter of days, after which it is fired at 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. A test is performed at this point, making sure there are no cracks in the object. This is followed by an initial glazing process after which the hand-painted design is applied. This stage differs in length, dependent upon the intricacy of the design work involved. A final firing is performed. Before being offered for sell, a certification process is next on the agenda. This is to ensure that the piece meets regulations and the level of excellence in craftsmanship has been achieved. It is at this time, provided all conditions have been met, that the piece is stamped with the maker’s mark along with a registration number.
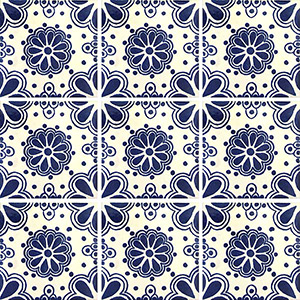
One characteristic of authentic Talavera pottery is the quality of detail in the painting, expertly applied. There is a raised appearance to the painted line, accompanied by a glossy sheen. Only natural earth pigments are used for the colors found in true Talavera. In its early days, the finest pottery was painted with a deep blue mineral, the most expensive pigment. This color motif, placed on the creamy white of the fired clay, was much sought after. It also provided a quality measure, reassuring the buyer that the piece they were purchasing was of the highest caliber. Other colors were introduced in 18th century, including yellow, green and mauve.
Today, when visiting the city of Puebla, you will be able to purchase authentic Talavera tiles, vases and dishes, along with many other fine Talavera objects. As well, you can see first-hand how Talavera tiles were used extensively in the decoration of the city’s historic churches, monasteries and ex-convents.
Article source: MexOnline.com